What is Vacuum clutch?
Vacuum clutch is the clutch operating system that uses the vacuum for engagement and disengagement of the clutch.
The vacuum used for this operation is taken from the engine intake manifold. The vacuum created inside the intake manifold is passed to the vacuum reservoir, through a non-return valve.
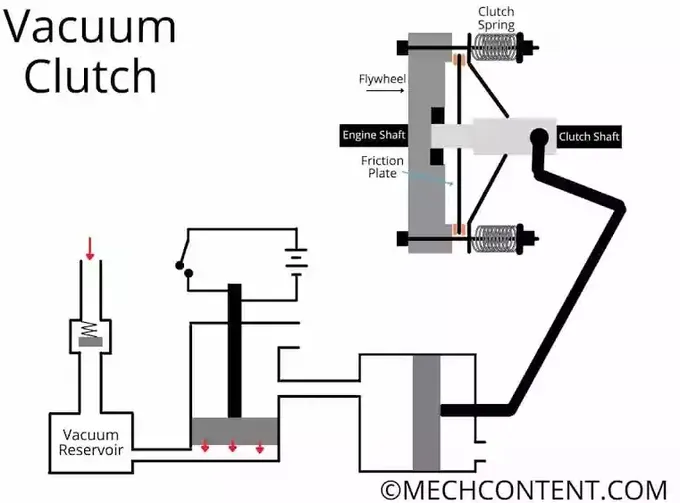
This system automatically operates when the driver shifts the gear. It means, during running the vehicle, when the driver shifts the gear, the system gets ON and disengages the clutch.
The benefit of using a vacuum clutch is that, the less effort is required to operate the clutch.
Contents:
Construction:
Vacuum clutch is consists of the following key components:
1) Engine Intake Manifold: It is responsible for creating vacuum inside the vacuum reservoir.
In an internal combustion engine, During the suction stroke of the piston, a vacuum is created in the intake manifold. Hence, vacuum from the manifold is transferred to the vacuum reservoir.
2) Non-Return Valve (NRV): It is a one-directional valve. The NRV allows, the vacuum from the manifold to transfer to the vacuum reservoir.
When manifold pressure is more than vacuum reservoir pressure, the NRV stops the reverse flow of vacuum to the intake manifold.
3) Vacuum Reservoir: Vacuum reservoir stores the vacuum that transferred from the manifold. This vacuum is used further to actuate the clutch.
4) Solenoid Valve: It is used to Start/Stop the flow of vacuum from vacuum reservoir to vacuum cylinder. The battery is used in the system to supply power to the solenoid valve.
5) Switch: Switch is used to Start/Stop the power supply to the solenoid valve. The switch is connected to the gear pedal.
When the driver presses the gear pedal, the switch gets ON and when the driver releases the gear pedal, the switch gets OFF.
6) Vacuum Cylinder: The vacuum line is connected to the cylinder to actuate the piston. The cylinder also has a vent on the opposite side of the piston to keep atmospheric pressure on one side.
7) Piston Rod: The piston rod is connected to the pressure plate of the Plate type clutch.
When the piston is pulled by vacuum, the pressure plate also gets pulled against the compressing spring.
Hence, pressure on the friction plate removes, so the friction plate releases from the flywheel therefore clutch gets disengage.
Working of vacuum clutch:
The engagement and disengagement of the vacuum-operated clutch is done as follows:
Disengagement:
When a vehicle is running, the clutch is in the engaged position. As soon as the driver press the gear pedal, the switch gets on and the power supply to the solenoid starts. Thus, the solenoid is pulled upward.
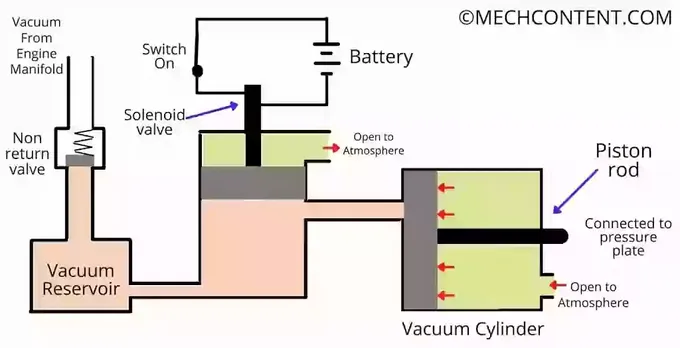
Due to the upward movement of the solenoid, the vacuum reservoir gets connected to the vacuum cylinder. Due to the vacuum, the piston moves (attracts) to left, due to the pressure difference between both side of the piston (Vacuum on left and atmospheric pressure on right).
When the piston moves to the left side, the pressure plate also moves to the left side. Hence, the pressure on the friction plate gets removed, so the friction plate releases from the flywheel, and the clutch gets Disengaged.
Engagement:
When the driver releases the gear pedal, the switch becomes OFF and the power supply to the solenoid valve gets stopped. Hence, solenoid came to its initial position.
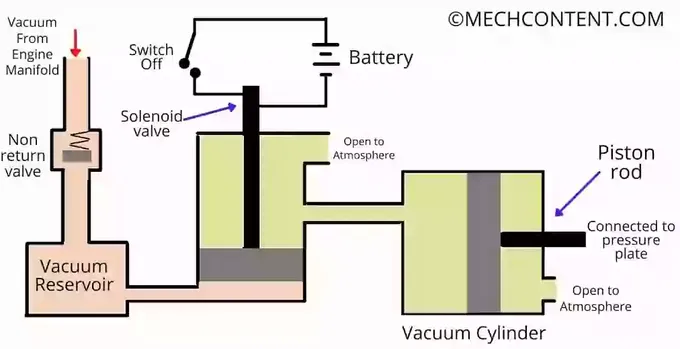
Due to the movement of the solenoid, the vacuum reservoir gets disconnected from the vacuum cylinder. Thus, pressure on both sides of the piston becomes the same. (atmospheric pressure).
Due to this, the piston returns to the original position. The pressure plate also moves to its initial state by the force of compressed spring. And clutch gets Engage.
Advantage of vacuum clutch:
The vacuum clutch has the following advantage
1] less effort is required to operate the clutch.
FAQ:
-
How does a vacuum clutch work?
The vacuum clutch is actuated using a vacuum from the intake manifold.
Read also